A SaaS Marketing Agency Approach to Conversions
Are you struggling to convert leads into paying customers for your SaaS business? Look no further than a SaaS marketing agency to help you improve...
Easy Personal Loans Simplified Through Loan Apps
The digital transformation has permeated every facet of our lives, and the financial sector is no exception. With the explosion of technology, personal finance management...
10 SaaS Marketing Agency Strategies You Should Implement
The SaaS (Software as a Service) market is more competitive than ever, with new products and startups launching every day. Having a great product is...
IT Consulting in San Diego: Empowering Businesses to Thrive in a Digital World
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses across industries are increasingly dependent on technology to drive growth, streamline operations, and deliver excellent customer service. With technology...
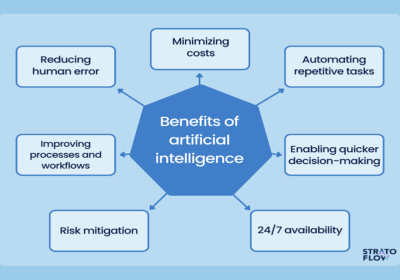
The Advantages of AI-Powered ID Card Scanners in Document Processing
In today’s fast-paced digital world, the demand for efficient and secure document processing is at an all-time high. Businesses across various sectors are adopting innovative...
CircuitMaker 2.2.1.6 Gerber Generation: A Step-by-Step Guide
CircuitMaker has been released by Altium as a free PCB design application that has all the needed capabilities and is easy to work with which...
Leveraging Electronic Identification for Digital Identification Technology in Asset Finance
Much like the initial skepticism towards credit cards when they were first introduced, there has been some apprehension over the use of electronic identification (e-ID)...
Common Areas Where Hotel Management Makes Mistakes
When you speak of hotel management, it is a multifaceted industry that demands detailed and careful attention to diverse types of operational aspects to ensure...
How Can Columbus Startups Leverage Custom Website Development for Growth?
The business world never rests. Every startup is trying its best to make a mark, gain the attention of its potential customers, and grow its...
Maximizing Sales: How Magento 2 Instagram Shop Extension Boosts Your E-commerce Business?
In the ever-evolving landscape of e-commerce, staying ahead of the curve is imperative for businesses looking to thrive in the digital marketplace. With the rise...